Emotional intelligence (EI) is a critical skill that goes beyond traditional cognitive abilities, shaping how we understand and manage our emotions and those of others. This article delves into the concept of Emotional Quotient (EQ), the measurable aspect of EI, and explores its profound impact on both personal and professional success. By examining the core components of EI—such as self-awareness, self-regulation, and empathy—we uncover how these skills contribute to personal growth, enhance leadership capabilities, and foster healthier relationships. Additionally, we’ll discuss practical strategies for developing EI and the tools available for assessing and strengthening this invaluable trait, ultimately unlocking the full potential of emotional intelligence in our lives.
Join weninsure.xyz as we delve deeper into this topic.
1. Definition and Importance of Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Emotional Intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and influence emotions—both your own and those of others. Unlike traditional intelligence, which is often measured by cognitive abilities such as logic, reasoning, and problem-solving, EI focuses on the softer skills that govern interpersonal relationships and self-awareness.
The importance of EI lies in its profound impact on various aspects of life. Individuals with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to handle stress, navigate social complexities, and make decisions that consider both rational and emotional factors. In the workplace, EI is essential for effective leadership, teamwork, and conflict resolution. It helps in building strong relationships, fostering a positive work environment, and improving overall job satisfaction. On a personal level, EI contributes to mental well-being, resilience, and the ability to maintain fulfilling relationships. As such, emotional intelligence is not just an advantageous skill but a crucial component for

2. Emotional Quotient (EQ): Measuring Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Quotient (EQ) is the metric used to quantify an individual’s emotional intelligence. Unlike IQ, which measures cognitive abilities, EQ assesses how well a person can identify, understand, manage, and influence emotions in themselves and others. The concept of EQ has gained prominence as research shows that emotional intelligence plays a vital role in personal and professional success.
Measuring EQ typically involves various assessments that evaluate key components of emotional intelligence, such as self-awareness, empathy, emotional regulation, and social skills. These assessments might include self-report questionnaires, 360-degree feedback from peers and colleagues, or behavioral observations. Popular tools like the Emotional Competence Inventory (ECI) or the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) provide insights into an individual’s emotional strengths and areas for improvement.
High EQ is often associated with better leadership capabilities, improved teamwork, and greater resilience in the face of challenges. By measuring EQ, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their emotional landscape, enabling them to develop targeted strategies for enhancing their emotional intelligence and, consequently, their overall effectiveness in various life domains.
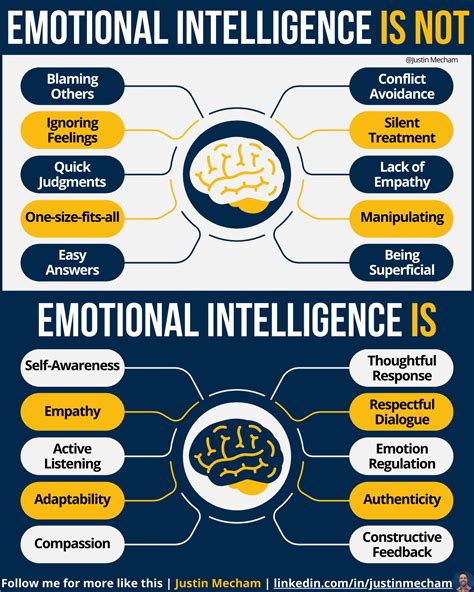
3. Core Components of EI: Self-Awareness, Self-Regulation, Motivation, Empathy, and Social Skills
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is composed of five core components: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.
Self-awareness involves recognizing and understanding one’s emotions, strengths, and limitations. This awareness allows individuals to assess how their feelings affect their thoughts and behaviors.
Self-regulation refers to the ability to manage and control emotions, particularly in stressful situations. It helps individuals remain composed and thoughtful in their responses.
Motivation within EI is driven by internal goals rather than external rewards. It fosters resilience and a positive outlook, driving individuals to pursue their objectives persistently.
Empathy is the capacity to understand and share the feelings of others. It enhances relationships by promoting compassion and effective communication.
Social skills encompass the ability to build and maintain relationships, manage conflict, and inspire others. Mastery of these skills enables effective collaboration and leadership, making them essential for bot

4. The Role of EI in Personal Growth and Well-being
Emotional Intelligence (EI) plays a crucial role in personal growth and well-being by enhancing one’s ability to navigate the complexities of life with emotional awareness and resilience. Individuals with high EI are better equipped to understand their own emotions, leading to greater self-acceptance and personal clarity. This self-awareness allows for more informed decision-making, as individuals can align their choices with their true values and goals.
Moreover, EI contributes significantly to emotional well-being. By practicing self-regulation, individuals can manage stress and anxiety more effectively, preventing emotional reactions from overwhelming their judgment. This emotional balance fosters a sense of inner peace and stability, which is essential for mental health.
Empathy, another core component of EI, deepens interpersonal relationships, which are fundamental to personal happiness. Understanding and responding to the emotions of others cultivates trust and intimacy, enhancing the quality of personal connections. These strong relationships provide a support system that is vital for emotional well-being.
Additionally, the motivation aspect of EI encourages a growth mindset, driving individuals to pursue self-improvement and resilience in the face of setbacks. This proactive approach to personal development leads to a more fulfilling life, as individuals continuously strive for progress and self-actualization. Ultimately, EI is a key factor in achieving both emotional health and personal growth.
5. How EI Enhances Leadership and Workplace Effectiveness
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a critical factor in enhancing leadership and workplace effectiveness. Leaders with high EI are better equipped to understand and manage their own emotions, as well as the emotions of their team members. This emotional insight fosters a supportive work environment where individuals feel valued and understood, leading to increased morale and productivity.
Self-awareness and self-regulation allow leaders to remain calm and composed under pressure, making thoughtful decisions that benefit the entire organization. Empathy enables leaders to connect with their team on a deeper level, understanding their needs and concerns, which is essential for building trust and loyalty.
Moreover, strong social skills help leaders communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and inspire and motivate their teams. This creates a collaborative atmosphere where employees are encouraged to contribute their best efforts. In turn, organizations with emotionally intelligent leaders often see improved performance, reduced turnover, and a positive workplace culture
6. Practical Strategies for Developing and Improving EI
Developing and improving Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a continuous process that can significantly enhance personal and professional life. One practical strategy is to cultivate self-awareness by regularly reflecting on your emotions and their impact on your thoughts and actions. Keeping a journal or engaging in mindfulness practices can help you become more attuned to your emotional states.
Self-regulation can be strengthened by practicing emotional control in challenging situations. Techniques such as deep breathing, pausing before responding, and cognitive reframing can help manage impulsive reactions and maintain composure.
Enhancing empathy involves actively listening to others and trying to understand their perspectives without judgment. Engaging in conversations with diverse individuals can broaden your emotional understanding and improve your ability to connect with others.
To boost motivation, set personal and professional goals that align with your core values. Break these goals into manageable steps and celebrate progress to maintain momentum and a positive outlook.
Finally, developing social skills is crucial for effective communication and relationship-building. Practice active listening, clear communication, and conflict resolution techniques to improve your interactions with others. Seeking feedback from peers and mentors can also provide valuable insights into areas for improvement. By consistently applying these strategies, you can enhance your EI and achieve greater success in various aspects of life.
7. The Impact of High EQ on Relationship Building and Conflict Resolution
High Emotional Quotient (EQ) profoundly impacts relationship building and conflict resolution by fostering deeper, more meaningful connections and facilitating effective problem-solving. Individuals with high EQ excel in understanding and managing their own emotions as well as those of others, which is crucial for building strong interpersonal relationships. They can navigate social complexities with empathy and clear communication, enhancing trust and rapport with colleagues, friends, and family.
In relationship building, high EQ enables individuals to respond to others’ emotions with sensitivity and compassion, which strengthens bonds and promotes mutual respect. This empathy helps in recognizing and addressing the needs and concerns of others, leading to more harmonious interactions.
When it comes to conflict resolution, high EQ individuals are adept at remaining calm and composed, even in tense situations. Their ability to empathize with differing viewpoints and communicate effectively allows them to address disagreements constructively. They can facilitate compromises and find solutions that satisfy all parties involved, reducing the potential for conflict escalation and fostering a collaborative atmosphere. Overall, high EQ enhances both the quality of relationships and the effectiveness of resolving disputes, leading to more p
8. Tools and Assessments for Evaluating and Strengthening EI
Evaluating and strengthening Emotional Intelligence (EI) can be effectively achieved through various tools and assessments designed to provide insights and guide development. One commonly used tool is the Emotional Competence Inventory (ECI), which assesses key EI components such as self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. The ECI offers a comprehensive evaluation based on self-report and feedback from others, providing a detailed profile of an individual’s emotional strengths and areas for growth.
Another popular assessment is the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT), which measures EI through a series of tasks that evaluate the ability to perceive, use, understand, and manage emotions. This test provides objective insights into emotional functioning and helps identify specific areas for improvement.
Additionally, 360-degree feedback tools involve gathering input from peers, subordinates, and supervisors to gain a well-rounded perspective on emotional competencies. This feedback can highlight how one’s emotional behaviors impact others and identify opportunities for development.
To complement these assessments, various self-help resources such as books, online courses, and coaching programs can support the enhancement of EI skills. Engaging in targeted training and reflection based on assessment results helps individuals develop a higher EQ and apply these skills more effectively in personal and prof
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a vital skill set that significantly impacts personal growth, workplace effectiveness, and relationship building. By understanding and enhancing key components such as self-awareness, empathy, and social skills, individuals can improve their emotional functioning and overall success. Utilizing to
weninsure.xyz

